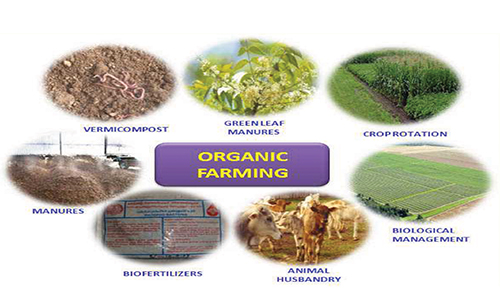
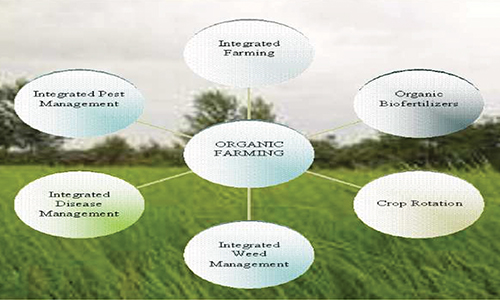
What is Organic Farming
Organic farming system in India is not new and is being followed from ancient time. It is a method of farming system which primarily aimed at ultivating the land and raising crops in such a way, as to keep the soil alive and in good health by use of organic wastes (crop, animal and farm wastes, aquatic wastes) and other biological materials along with beneficial microbes (bio fertilizers) to release nutrients to crops for increased sustainable production in an eco friendly pollution free environment.
Need Of Organic Farming
With the increase in population our compulsion would be not only to stabilize agricultural production but to increase it further in sustainable manner. The scientists have realized that the ‘Green Revolution’ with high inp ut use has reached a plateau and is now sustained with diminishing return of falling dividends.
Thus, a natural balance needs to be maintaine d at all cost for existence of life and property. The obvious choice for that would be more relevant in the present era, when these agrochemicals which are produced from fossil fuel and are not renewable and are diminishing in availability. It may also cost heavily on our foreign exchange in future.
Characteristics of Organic Farming
The key characteris tics of Organic Farming include,
- Protecting the long term fertility of soils by maintaining organic matter levels , encouraging soil biological activity, and care ful mechanical intervention
- Providing crop nutrients indirectly using relatively insoluble nutrient sources which are made available to the plant by the action of soilmicro-organisms
- Nitrogen self-sufficiency through the use of legumes and biological nitrogen fixation, as well as effective recycling of organic materials including crop residues and livestockmanures.
- Weed, disease and pest control relying primarily on crop rotations, natural predators, diversity, organic manuring, resistant varieties and limited (preferably minimal) thermal, biological and chemical intervention
- The extensive management of livestock, paying full regard to their evolutionary adaptations, behavioural needs and animal welfare issueswith respect to nutrition, housing, health, breeding and rearing
- Careful attention to the impact of the farming systemon the wider environment and the conservation of wildlife and natural habitats
Composting
Compost has many advantages over chemical fertilizers. These provide nutrients for plants but do not improve soil structure. They usually only improve yields in the season in which they are applied. Because compost feeds soil life and improves soil structure, the beneficial effects are long lasting
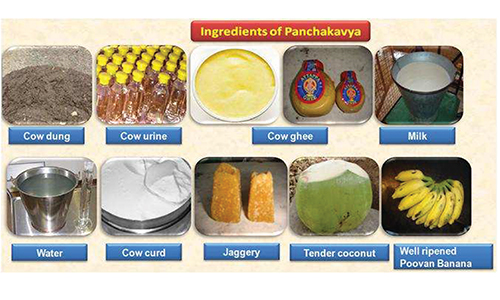
‘Panchagavya’ Preparation
‘Panchagavya’ is one such organic product for plants. It is a Organic Plant Liquid Fertilizer. It is a Organic growth Stimultant for all types of plants, Milch Animals, Goat, Poultry, Fish, Pet Animals etc.,
Panchagavya is also a traditional method, used to safeguard plants and soil micro-organisms and to increase plant production.
Panchagavya application is found to be more profitable than recommended fertilizer application and chemical spray. The modified versions used for organic farming have been standarised by experimental trials.
Mulching
Mulching means covering the ground with a layer of loose material such as compost ,manure ,straw ,dry grass , leaves or crop residues.
Our Future Plan – Green House
A greenhouse is a structure that produces a microclimate ideal for plant growth. It can be used for planting or house them throughout their life.